FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions
Sort by Topic
FAQs
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a wireless protocol designed for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWAN) that enables long-range communication with low power consumption. LoRaWAN is based on LoRa (Long Range) modulation technology, which enables communication over distances of several kilometers in rural or suburban areas with low power consumption.
LoRaWAN operates in unlicensed frequency bands, making it accessible to anyone, and is suitable for a wide range of IoT (Internet of Things) applications such as smart cities, agriculture, environmental monitoring, asset tracking, and more.
LoRaWAN uses a star topology, where end devices communicate directly with a central gateway or base station. The gateway then relays the data to a network server, which can process and analyze the data, and send commands back to the end devices.
One of the key features of LoRaWAN is its ability to support various classes of devices, depending on their power requirements and communication needs. Class A devices are the most common and operate on a strict bi-directional communication schedule, where the device listens for incoming data only after it has sent a transmission. Class B devices add an additional reception window at predetermined times to enable scheduled downlink communication from the gateway. Class C devices operate with the lowest power consumption and have the most flexible bi-directional communication schedule.
LoRaWAN is an open standard, managed by the LoRa Alliance, which is a non-profit organization that promotes and develops the technology. There are many LoRaWAN-compatible devices and solutions available from a variety of vendors, making it a popular choice for IoT applications.
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, long-range wireless protocol that is designed for IoT applications in which devices are spread over large areas. Here are some of the benefits of LoRaWAN:
- Long-range coverage: LoRaWAN can transmit data over several kilometers, making it ideal for applications in which devices are spread out over a large area.
- Low power consumption: LoRaWAN uses very little power, which means that devices can operate for long periods of time without needing to be recharged or replaced.
- Low cost: LoRaWAN is a relatively low-cost solution, which makes it accessible to a wide range of users and applications.
- Easy to deploy: LoRaWAN is easy to deploy and manage, which makes it an attractive solution for applications in which devices are difficult to access.
- Secure: LoRaWAN uses AES encryption to ensure the security of transmitted data.
The history of LoRaWAN dates back to 2011, when it was first developed by Cycleo, a French semiconductor company. In 2012, Cycleo was acquired by Semtech, a US-based semiconductor company, which continued to develop and promote the technology. In 2015, the LoRa Alliance was formed, with the goal of promoting and standardizing the use of LoRaWAN technology. Today, the LoRa Alliance has over 500 members and is one of the largest IoT alliances in the world. LoRaWAN is used in a wide range of applications, including smart cities, agriculture, and industrial IoT.
There are several IoT protocols in use today, each with its own strengths and use cases. Here are some of the most common IoT protocols and their typical use cases:
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): MQTT is a lightweight protocol that is ideal for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks, such as those used in IoT devices. It is commonly used for remote monitoring and control applications, such as tracking sensor data from a remote location.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): HTTP is a widely used protocol for transmitting data over the internet, and it can also be used for IoT applications. HTTP is often used for applications that require higher bandwidth, such as video streaming or real-time data analytics.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): CoAP is a protocol that is designed for use in constrained environments, such as those with low power or limited processing capabilities. It is commonly used in applications such as smart homes and industrial IoT.
- DDS (Data Distribution Service): DDS is a protocol that is designed for high-performance, real-time systems. It is commonly used in industrial IoT applications, such as those used in manufacturing and transportation.
- Zigbee: Zigbee is a wireless protocol that is commonly used for smart home applications, such as home automation and security systems. It is designed for low-power devices and can be used to create mesh networks, which can help improve reliability and coverage.
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network): LoRaWAN is a low-power, long-range protocol that is commonly used for IoT applications in which devices are spread over large areas, such as smart cities and agriculture. It can transmit data over long distances with low power consumption.
These are just a few of the many IoT protocols that are currently in use. The choice of protocol depends on the specific application and the requirements of the system.
The LoRa Alliance® is a non-profit association of more than 500 member companies from around the world, focused on the advancement of the LoRaWAN® standard for low power wide area networks (LPWANs). LPWANs provide long-range, low-power connectivity for IoT devices, enabling a wide range of applications in various industries, including smart cities, agriculture, industrial IoT, and more.
The LoRa Alliance was founded in 2015, and since then it has grown to become one of the leading organizations in the LPWAN space. The Alliance’s members come from a wide range of industries, including device manufacturers, network operators, system integrators, and application developers. The Alliance’s mission is to promote and standardize the LoRaWAN technology, which enables low-power, long-range communication for IoT devices.
One of the key benefits of the LoRaWAN technology is its ability to provide long-range connectivity while using very little power. This makes it ideal for IoT devices that need to operate for extended periods of time without requiring frequent battery replacements. LoRaWAN can also operate over unlicensed radio spectrum, which makes it cost-effective and easy to deploy.
The LoRa Alliance works to promote and advance the LoRaWAN technology by developing and promoting standards, educating the market, and fostering collaboration between its members. The Alliance’s Technical Committee is responsible for developing and maintaining the LoRaWAN specification, while the Marketing Committee focuses on promoting the technology and educating the market.
The LoRa Alliance also works to certify devices and network infrastructure that conform to the LoRaWAN standard, ensuring interoperability and reliability. The Alliance’s certification program is open to all members, and it provides a rigorous testing process to ensure that devices and infrastructure meet the Alliance’s standards for performance and interoperability.
In addition to promoting and advancing the LoRaWAN technology, the LoRa Alliance also works to drive adoption and innovation in various industries. The Alliance has established various vertical market groups, focused on industries such as smart cities, industrial IoT, and agriculture, to drive innovation and collaboration among its members in these areas.
Overall, the LoRa Alliance is a critical organization in the LPWAN space, providing a platform for collaboration, standardization, and innovation. With its focus on promoting the LoRaWAN technology and driving adoption in various industries, the Alliance is helping to enable the next wave of IoT innovation and growth.
Wireless sensors are devices that collect sensory information from local environments. This hardware monitors its surroundings and detects changes in stimuli, such as air temperature, movement, lighting, and liquid leakage. They are programmed to interact with central gateways, hubs, and servers, with all nodes arranged to support the network developer’s objectives. Wireless sensors are usually distributed across large areas, and some networks contain anywhere from hundreds to thousands of them at one time.
IoT sensors measure specific elements of their surroundings and create outputs in the form of electrical signals that allow for further processing. Wireless sensor networks contain numerous geographically distributed sensors that interact and communicate through wireless connections. Common network sensors share information through gateways, which connect local IoT sensors to the Internet. Gateways act as both wireless access points and routers.
IoT wireless sensor technology has enabled applications across numerous industries, offering endless possibilities for IoT connectivity. Some of the many advantages of smart wireless sensors include:
- Real-time monitoring. Wireless sensors monitor their surroundings in real time, always providing up-to-date information.
- Risk minimization. Smart sensors pick up on irregular environmental stimuli such as leaks and temperature changes, minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Environmental maintenance. IoT sensors maintain favorable environments in the workplace, keeping track of elements such as the heat index and air quality.
- Long-lasting use. Wireless sensors can operate on a single battery for years without requiring charging or changing.
- Low maintenance. IoT sensors need very little maintenance, meaning you don’t have to worry about performing upkeep or scheduling repairs.
- Low power. Sensory hardware consumes low levels of power, which is why their batteries last for years at a time.
- Operative capabilities. Smart sensors can function on low-bandwidth networks due to their light data loads.
Our selection of wireless sensors works exceptionally well with LoRaWAN networks. LoRaWAN networks are popular for their ability to transmit data across long distances and excellent link margins that reach signals beneath the radio frequency (RF) noise floor. These networks make connections more accessible, proving useful for wireless sensors in remote areas without public access.
If you need IoT wireless sensors, MultiTech + Radio Bridge are your solution. As the leading LoRaWAN sensor manufacturer in North America, we’re always looking for ways to continue raising the bar in the IoT industry. Our sensors are built to last, embracing unbeatable functionality and efficiency across numerous applications. We also offer product customizations to better serve your organization’s needs. When you come to Radio Bridge for LoRaWAN wireless sensor solutions, we want you to have the best possible experience. That’s why we always strive to deliver excellent customer service that makes you feel comfortable and supported.
Definition of an IoT Gateway
At its simplest, an IoT gateway is an intelligent central hub for IoT devices. IoT gateways connect devices within the Internet of Things to one another and to the cloud, translating communication between the devices and filtering data into useful information.
A true IoT gateway contains communication technologies connecting end-devices (sensors, actuators or more complex devices) and backend platforms (data, device and subscriber management) to the gateway. It has a computing platform allowing pre-installed or user-defined applications to manage data (for routing and computing at edge), devices, security, communication and other aspects of the gateway.
If you or your company has invested in expanding your use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, you may have noticed the term “IoT Gateway” popping up more and more frequently.
But you might also have questions, including: what is an IoT gateway, what is the use of a gateway in IoT, and — most importantly — should you be investing in them?
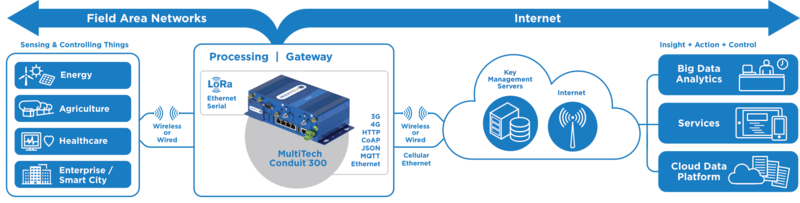
Some of the most common uses for IoT gateways include:
- Connecting devices to one another
- Connecting devices to the cloud
- Translating communicate between IoT devices that are manufactured or operated by different companies
- Filtering data
- Mitigating security risks
- Intelligence at the edge
Advantages of Using IoT Gateways
Whether your company is ready to invest heavily in IoT or wants to start with a few devices here and there, getting set up with IoT gateways will provide immediate and long-term advantages.
Connecting Devices to One Another and the Cloud
Think of IoT gateways like universal remotes. While you can have different remotes that all work with different devices, a universal remote allows you to control all of them from a central location, saving you time and effort. Without IoT gateways, your devices still work and can be controlled individually, but it’s more of a hassle and they can’t be programmed to work together.
As a centralized hub, an IoT gateway provides a single location where data is communicated to and from devices. This communication comes from other devices and users via the cloud. When you receive information or provide information to an IoT device—such as a change in protocol—you’re communicating with these devices through IoT gateways via cloud-enabled software.
IoT gateways are also able to connect to one another to streamline and expand their functionality throughout a physical location and in use with a growing number of IoT devices and smart sensors. By installing universal IoT gateways early in your technology plan, you can add devices seamlessly while saving time and effort.
Translating Communication Between IoT Devices
Although IoT devices are rapidly becoming a part of our everyday, with new products and services popping up all the time to aid in just about every aspect of our lives, standards for a common language between devices does not yet exist.
For example, while your office may have motion-sensor-enabled lighting and climate control, the lights and climate control are unlikely to be able to communicate with one another unless they are manufactured by the same company—or, unless you have IoT gateways translating information between them.
As more IoT devices are added, the more important hubs become in simplifying how they work together.
Filtering Data
Not only does IoT gateway allow your devices to speak to each other, but it simplifies the ways in which your IoT devices communicate by filtering data into useful bits of information. Because IoT devices can record new bits of data in a fraction of a second, seeing every record would be unhelpful and bog down how quickly the devices can work and communicate. IoT gateways are intelligent and able to work at the edge, meaning each gateway can think about and comb through the data provided then only send the necessary filtered data to the cloud, improving communication and response times.
Security and Risk Mitigation
As IoT devices expand, so do the security risks against them. You’ve likely heard horror stories of the Internet of Things run amok, including Wi-Fi baby monitors allowing hackers to listen in or smart cars going rogue. The ability for outside influence and hacking is possible with all IoT devices—but an IoT gateway provides another layer between the internet and the device itself. Even if your company isn’t going to be investing heavily in IoT, a gateway enables further investment in the future while providing extra security for IoT devices you already own.
Intelligence at the Edge
It’s important to note that IoT gateways are an example of “intelligence at the edge” or “intelligent edge.” This means data can be processed and understood by the IoT gateway itself, rather than requiring a third party or human to decipher and process the information. IoT gateways are themselves an example of the intelligent edge at play.
MultiTech’s IoT Gateways
MultiTech is a leader in developing and manufacturing cutting edge IoT devices and the electronics you need to have to get ahead in business today. Our IoT gateways are the latest in tech innovation and one of the centerpieces of our suite of products. If you’re ready to see what IoT gateways can best help you and your organization, check out our extensive portfolio.
Smart building IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental input and process that data in order to perform desired automated functions related to security, facilities management, or related property needs. Wireless MultiTech sensors that perform these functions include:
- Temperature sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Push button sensors
- Movement sensors
- Leak detection sensors
- Industrial sensors
MultiTech smart building IoT sensor technology can help lead to fewer errors, faster response times, improved compliance, decreased downtime, and ultimately, cost savings. That’s because our equipment enables:
- Wireless failover
- Wireline replacement
- Parallel networking
- Remote equipment management and control
- Facility automation
- Secure data transfer
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are small devices that collect and share data gathered from their surroundings within a technological ecosystem. Sometimes the sensor can act on the data immediately or the data can be sent to an IoT gateway that aggregates and sends the data where it needs to go for further action and analysis.
Smart building IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental input and process that data in order to perform desired automated functions related to security, facilities management, or related property needs. Wireless MultiTech sensors that perform these functions include:
- Temperature sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Push button sensors
- Movement sensors
- Leak detection sensors
- Industrial sensors
A smart building is a facility that uses advanced technology and data analytics to optimize its operations, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the occupant experience. Smart buildings use a variety of sensors, devices, and systems to collect and analyze data on building operations, energy consumption, and occupant behavior. This data is then used to make informed decisions about building management, energy usage, and maintenance.
Smart buildings can include a wide range of systems and technologies, including:
- Building automation systems (BAS): These systems control the building’s mechanical and electrical systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and security.
- Energy management systems (EMS): These systems optimize energy usage and reduce energy waste by monitoring and controlling energy consumption.
- Occupancy sensors: These sensors detect the presence of occupants and adjust building systems accordingly, such as turning off lights in unoccupied rooms.
- Environmental sensors: These sensors monitor indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity to ensure optimal comfort and health for occupants.
- Building analytics software: This software collects and analyzes data from building systems and sensors to identify inefficiencies, optimize operations, and predict maintenance needs.
Smart buildings offer a number of benefits, including:
- Improved energy efficiency: Smart buildings can reduce energy waste by optimizing energy consumption and reducing energy usage during times of low occupancy.
- Enhanced occupant comfort and productivity: By adjusting building systems based on occupant behavior and preferences, smart buildings can create a more comfortable and productive environment for occupants.
- Predictive maintenance: Smart buildings can identify maintenance needs before they become critical, reducing downtime and improving equipment lifespan.
- Cost savings: By optimizing energy usage and reducing maintenance costs, smart buildings can result in significant cost savings over time.
Smart buildings represent a growing trend in building design and management, offering a wide range of benefits for both building owners and occupants.
MNO (Mobile Network Operator) and MVNO (Mobile Virtual Network Operator) are terms used in the telecommunications industry to describe different types of companies that provide mobile communication services. They have distinct roles and relationships within the mobile ecosystem.
- Mobile Network Operator (MNO):
- An MNO is a company that owns and operates the physical infrastructure of a mobile network. This includes the cellular towers, base stations, switching centers, and other network elements required to provide wireless communication services.
- MNOs are the primary carriers that build, deploy, and maintain the cellular network infrastructure. They are responsible for managing network operations, ensuring coverage, and offering various mobile services.
- Examples of MNOs include major telecommunications companies like Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Vodafone. These companies often have a wide geographic presence and offer a range of mobile services directly to consumers and businesses.
- Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO):
- An MVNO is a company that offers mobile communication services to customers without owning the physical network infrastructure. Instead, MVNOs lease network capacity and services from existing MNOs.
- MVNOs essentially resell the connectivity provided by MNOs. They purchase wholesale access to the network’s capacity and then sell their own branded mobile services to customers.
- MVNOs have the flexibility to focus on specific niches or customer segments, and they often differentiate themselves through pricing, specialized services, or unique offerings.
- Examples of MVNOs include companies like Boost Mobile, Virgin Mobile, and Google Fi. These companies use existing network infrastructure to provide services without having to invest in building their own networks.
In summary, MNOs own and operate the physical cellular network infrastructure, while MVNOs lease network capacity from MNOs to provide mobile services to customers. MNOs are responsible for building and maintaining the network, while MVNOs focus on offering tailored services and experiences to their customers without the need for extensive infrastructure investments.
LPWAN stands for Low-power wide area networks, also known as LPWAN, are networks designed to facilitate long-range communication between technological devices at low bit rates. They are the connectivity option of choice for most IoT sensors, because they offer wide area coverage at low power consumption, making them less costly to both use and run.
 There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
LoRaWAN® is benefitted by its long range, deep penetration, and extended battery life. LoRaWAN standards are maintained by the LoRa Alliance, an open, non-profit association dedicated to promoting and supporting their global adoption.
The ability for these sensors to provide ultra long range communications to industry standard gateways is one of their biggest benefits. For example, MultiTech offers LoRaWAN IoT sensors as part of their Radio Bridge family of products including:, which includes:
- Wireless temperature sensors designed to accurately detect ambient air temperatures both indoors and out
- Wireless proximity sensors that provide high accuracy proximity detection with open architecture for flexible integration
- Wireless push button sensors that can be used as wearables, remote controls, or for emergency response and other button-push applications
- Wireless movement sensors that use ultra-sensitive internal accelerometers to detect movement or utilization of critical assets and react accordingly
- Wireless leak detection sensors that use probes to detect the presence of water and alert the network to divert potential catastrophe
- Wireless industrial sensors designed for industrial standards such as 4-20mA current loops, digital inputs, vibration and beyond
LoRaWAN IoT sensors low power consumption and long range transmit capabilities allow them to be used in a broad range of applications.
Here are some common use cases:
- Smart buildings. Modern offices, retail spaces, and factories can all benefit from smart building technology, including: temperature and humidity monitoring of critical rooms or assets, water leak detection to minimize leaking water or flood damage, motion detection to track utilization of high cost assets and more.
- Server room maintenance. Leak detection sensors can communicate automatically over wireless networks to notify IT managers when a leak is found in their liquid cooled server room, saving both precious data and precious dollars. Temperature sensing can ensure that critical IT equipment stays within its recommended operating ranges.
- Drug management. Readmission rates can be reduced and health outcomes improved via smart drug management and medication tracking using IoT sensors. Automated temperature monitoring of stored medications may improve medicine safety, effectiveness and compliance.
- Emergency response. Wireless push button sensors can be used in healthcare settings to allow nurses and caregivers to be alerted and respond to emergency patient needs in real time.
- Wind monitoring and control. Being able to monitor wind and solar energy generation in real time can prevent downtime and disruption, reducing risk and cost.
- Supply chain management. The right network solutions can help with shipment verification, remote monitoring of product storage, and the efficiency of logistical operations. That in turn leads to fewer shipping delays, less product loss, and happier customers.
- The benefits of using LoRaWAN IoT sensors are vast and unique to each industry they serve. All business applications of this technology lead to improved response time, improved compliance, decreased network downtime, performance data gathering, and ultimately–cost savings.
Check out MultiTech’s wireless LoRaWAN Sensor catalog for a closer look at this efficiency-boosting technology.
LoRaWAN
LPWAN stands for Low-power wide area networks, also known as LPWAN, are networks designed to facilitate long-range communication between technological devices at low bit rates. They are the connectivity option of choice for most IoT sensors, because they offer wide area coverage at low power consumption, making them less costly to both use and run.
 There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
LoRaWAN® is benefitted by its long range, deep penetration, and extended battery life. LoRaWAN standards are maintained by the LoRa Alliance, an open, non-profit association dedicated to promoting and supporting their global adoption.
The ability for these sensors to provide ultra long range communications to industry standard gateways is one of their biggest benefits. For example, MultiTech offers LoRaWAN IoT sensors as part of their Radio Bridge family of products including:, which includes:
- Wireless temperature sensors designed to accurately detect ambient air temperatures both indoors and out
- Wireless proximity sensors that provide high accuracy proximity detection with open architecture for flexible integration
- Wireless push button sensors that can be used as wearables, remote controls, or for emergency response and other button-push applications
- Wireless movement sensors that use ultra-sensitive internal accelerometers to detect movement or utilization of critical assets and react accordingly
- Wireless leak detection sensors that use probes to detect the presence of water and alert the network to divert potential catastrophe
- Wireless industrial sensors designed for industrial standards such as 4-20mA current loops, digital inputs, vibration and beyond
LoRaWAN IoT sensors low power consumption and long range transmit capabilities allow them to be used in a broad range of applications.
Here are some common use cases:
- Smart buildings. Modern offices, retail spaces, and factories can all benefit from smart building technology, including: temperature and humidity monitoring of critical rooms or assets, water leak detection to minimize leaking water or flood damage, motion detection to track utilization of high cost assets and more.
- Server room maintenance. Leak detection sensors can communicate automatically over wireless networks to notify IT managers when a leak is found in their liquid cooled server room, saving both precious data and precious dollars. Temperature sensing can ensure that critical IT equipment stays within its recommended operating ranges.
- Drug management. Readmission rates can be reduced and health outcomes improved via smart drug management and medication tracking using IoT sensors. Automated temperature monitoring of stored medications may improve medicine safety, effectiveness and compliance.
- Emergency response. Wireless push button sensors can be used in healthcare settings to allow nurses and caregivers to be alerted and respond to emergency patient needs in real time.
- Wind monitoring and control. Being able to monitor wind and solar energy generation in real time can prevent downtime and disruption, reducing risk and cost.
- Supply chain management. The right network solutions can help with shipment verification, remote monitoring of product storage, and the efficiency of logistical operations. That in turn leads to fewer shipping delays, less product loss, and happier customers.
- The benefits of using LoRaWAN IoT sensors are vast and unique to each industry they serve. All business applications of this technology lead to improved response time, improved compliance, decreased network downtime, performance data gathering, and ultimately–cost savings.
Check out MultiTech’s wireless LoRaWAN Sensor catalog for a closer look at this efficiency-boosting technology.
MultiTech Products
Definition of an IoT Gateway
At its simplest, an IoT gateway is an intelligent central hub for IoT devices. IoT gateways connect devices within the Internet of Things to one another and to the cloud, translating communication between the devices and filtering data into useful information.
A true IoT gateway contains communication technologies connecting end-devices (sensors, actuators or more complex devices) and backend platforms (data, device and subscriber management) to the gateway. It has a computing platform allowing pre-installed or user-defined applications to manage data (for routing and computing at edge), devices, security, communication and other aspects of the gateway.
If you or your company has invested in expanding your use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, you may have noticed the term “IoT Gateway” popping up more and more frequently.
But you might also have questions, including: what is an IoT gateway, what is the use of a gateway in IoT, and — most importantly — should you be investing in them?

Some of the most common uses for IoT gateways include:
- Connecting devices to one another
- Connecting devices to the cloud
- Translating communicate between IoT devices that are manufactured or operated by different companies
- Filtering data
- Mitigating security risks
- Intelligence at the edge
Advantages of Using IoT Gateways
Whether your company is ready to invest heavily in IoT or wants to start with a few devices here and there, getting set up with IoT gateways will provide immediate and long-term advantages.
Connecting Devices to One Another and the Cloud
Think of IoT gateways like universal remotes. While you can have different remotes that all work with different devices, a universal remote allows you to control all of them from a central location, saving you time and effort. Without IoT gateways, your devices still work and can be controlled individually, but it’s more of a hassle and they can’t be programmed to work together.
As a centralized hub, an IoT gateway provides a single location where data is communicated to and from devices. This communication comes from other devices and users via the cloud. When you receive information or provide information to an IoT device—such as a change in protocol—you’re communicating with these devices through IoT gateways via cloud-enabled software.
IoT gateways are also able to connect to one another to streamline and expand their functionality throughout a physical location and in use with a growing number of IoT devices and smart sensors. By installing universal IoT gateways early in your technology plan, you can add devices seamlessly while saving time and effort.
Translating Communication Between IoT Devices
Although IoT devices are rapidly becoming a part of our everyday, with new products and services popping up all the time to aid in just about every aspect of our lives, standards for a common language between devices does not yet exist.
For example, while your office may have motion-sensor-enabled lighting and climate control, the lights and climate control are unlikely to be able to communicate with one another unless they are manufactured by the same company—or, unless you have IoT gateways translating information between them.
As more IoT devices are added, the more important hubs become in simplifying how they work together.
Filtering Data
Not only does IoT gateway allow your devices to speak to each other, but it simplifies the ways in which your IoT devices communicate by filtering data into useful bits of information. Because IoT devices can record new bits of data in a fraction of a second, seeing every record would be unhelpful and bog down how quickly the devices can work and communicate. IoT gateways are intelligent and able to work at the edge, meaning each gateway can think about and comb through the data provided then only send the necessary filtered data to the cloud, improving communication and response times.
Security and Risk Mitigation
As IoT devices expand, so do the security risks against them. You’ve likely heard horror stories of the Internet of Things run amok, including Wi-Fi baby monitors allowing hackers to listen in or smart cars going rogue. The ability for outside influence and hacking is possible with all IoT devices—but an IoT gateway provides another layer between the internet and the device itself. Even if your company isn’t going to be investing heavily in IoT, a gateway enables further investment in the future while providing extra security for IoT devices you already own.
Intelligence at the Edge
It’s important to note that IoT gateways are an example of “intelligence at the edge” or “intelligent edge.” This means data can be processed and understood by the IoT gateway itself, rather than requiring a third party or human to decipher and process the information. IoT gateways are themselves an example of the intelligent edge at play.
MultiTech’s IoT Gateways
MultiTech is a leader in developing and manufacturing cutting edge IoT devices and the electronics you need to have to get ahead in business today. Our IoT gateways are the latest in tech innovation and one of the centerpieces of our suite of products. If you’re ready to see what IoT gateways can best help you and your organization, check out our extensive portfolio.
Sensor FAQ's
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a wireless protocol designed for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWAN) that enables long-range communication with low power consumption. LoRaWAN is based on LoRa (Long Range) modulation technology, which enables communication over distances of several kilometers in rural or suburban areas with low power consumption.
LoRaWAN operates in unlicensed frequency bands, making it accessible to anyone, and is suitable for a wide range of IoT (Internet of Things) applications such as smart cities, agriculture, environmental monitoring, asset tracking, and more.
LoRaWAN uses a star topology, where end devices communicate directly with a central gateway or base station. The gateway then relays the data to a network server, which can process and analyze the data, and send commands back to the end devices.
One of the key features of LoRaWAN is its ability to support various classes of devices, depending on their power requirements and communication needs. Class A devices are the most common and operate on a strict bi-directional communication schedule, where the device listens for incoming data only after it has sent a transmission. Class B devices add an additional reception window at predetermined times to enable scheduled downlink communication from the gateway. Class C devices operate with the lowest power consumption and have the most flexible bi-directional communication schedule.
LoRaWAN is an open standard, managed by the LoRa Alliance, which is a non-profit organization that promotes and develops the technology. There are many LoRaWAN-compatible devices and solutions available from a variety of vendors, making it a popular choice for IoT applications.
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, long-range wireless protocol that is designed for IoT applications in which devices are spread over large areas. Here are some of the benefits of LoRaWAN:
- Long-range coverage: LoRaWAN can transmit data over several kilometers, making it ideal for applications in which devices are spread out over a large area.
- Low power consumption: LoRaWAN uses very little power, which means that devices can operate for long periods of time without needing to be recharged or replaced.
- Low cost: LoRaWAN is a relatively low-cost solution, which makes it accessible to a wide range of users and applications.
- Easy to deploy: LoRaWAN is easy to deploy and manage, which makes it an attractive solution for applications in which devices are difficult to access.
- Secure: LoRaWAN uses AES encryption to ensure the security of transmitted data.
The history of LoRaWAN dates back to 2011, when it was first developed by Cycleo, a French semiconductor company. In 2012, Cycleo was acquired by Semtech, a US-based semiconductor company, which continued to develop and promote the technology. In 2015, the LoRa Alliance was formed, with the goal of promoting and standardizing the use of LoRaWAN technology. Today, the LoRa Alliance has over 500 members and is one of the largest IoT alliances in the world. LoRaWAN is used in a wide range of applications, including smart cities, agriculture, and industrial IoT.
There are several IoT protocols in use today, each with its own strengths and use cases. Here are some of the most common IoT protocols and their typical use cases:
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): MQTT is a lightweight protocol that is ideal for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks, such as those used in IoT devices. It is commonly used for remote monitoring and control applications, such as tracking sensor data from a remote location.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): HTTP is a widely used protocol for transmitting data over the internet, and it can also be used for IoT applications. HTTP is often used for applications that require higher bandwidth, such as video streaming or real-time data analytics.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): CoAP is a protocol that is designed for use in constrained environments, such as those with low power or limited processing capabilities. It is commonly used in applications such as smart homes and industrial IoT.
- DDS (Data Distribution Service): DDS is a protocol that is designed for high-performance, real-time systems. It is commonly used in industrial IoT applications, such as those used in manufacturing and transportation.
- Zigbee: Zigbee is a wireless protocol that is commonly used for smart home applications, such as home automation and security systems. It is designed for low-power devices and can be used to create mesh networks, which can help improve reliability and coverage.
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network): LoRaWAN is a low-power, long-range protocol that is commonly used for IoT applications in which devices are spread over large areas, such as smart cities and agriculture. It can transmit data over long distances with low power consumption.
These are just a few of the many IoT protocols that are currently in use. The choice of protocol depends on the specific application and the requirements of the system.
The LoRa Alliance® is a non-profit association of more than 500 member companies from around the world, focused on the advancement of the LoRaWAN® standard for low power wide area networks (LPWANs). LPWANs provide long-range, low-power connectivity for IoT devices, enabling a wide range of applications in various industries, including smart cities, agriculture, industrial IoT, and more.
The LoRa Alliance was founded in 2015, and since then it has grown to become one of the leading organizations in the LPWAN space. The Alliance’s members come from a wide range of industries, including device manufacturers, network operators, system integrators, and application developers. The Alliance’s mission is to promote and standardize the LoRaWAN technology, which enables low-power, long-range communication for IoT devices.
One of the key benefits of the LoRaWAN technology is its ability to provide long-range connectivity while using very little power. This makes it ideal for IoT devices that need to operate for extended periods of time without requiring frequent battery replacements. LoRaWAN can also operate over unlicensed radio spectrum, which makes it cost-effective and easy to deploy.
The LoRa Alliance works to promote and advance the LoRaWAN technology by developing and promoting standards, educating the market, and fostering collaboration between its members. The Alliance’s Technical Committee is responsible for developing and maintaining the LoRaWAN specification, while the Marketing Committee focuses on promoting the technology and educating the market.
The LoRa Alliance also works to certify devices and network infrastructure that conform to the LoRaWAN standard, ensuring interoperability and reliability. The Alliance’s certification program is open to all members, and it provides a rigorous testing process to ensure that devices and infrastructure meet the Alliance’s standards for performance and interoperability.
In addition to promoting and advancing the LoRaWAN technology, the LoRa Alliance also works to drive adoption and innovation in various industries. The Alliance has established various vertical market groups, focused on industries such as smart cities, industrial IoT, and agriculture, to drive innovation and collaboration among its members in these areas.
Overall, the LoRa Alliance is a critical organization in the LPWAN space, providing a platform for collaboration, standardization, and innovation. With its focus on promoting the LoRaWAN technology and driving adoption in various industries, the Alliance is helping to enable the next wave of IoT innovation and growth.
Wireless sensors are devices that collect sensory information from local environments. This hardware monitors its surroundings and detects changes in stimuli, such as air temperature, movement, lighting, and liquid leakage. They are programmed to interact with central gateways, hubs, and servers, with all nodes arranged to support the network developer’s objectives. Wireless sensors are usually distributed across large areas, and some networks contain anywhere from hundreds to thousands of them at one time.
IoT sensors measure specific elements of their surroundings and create outputs in the form of electrical signals that allow for further processing. Wireless sensor networks contain numerous geographically distributed sensors that interact and communicate through wireless connections. Common network sensors share information through gateways, which connect local IoT sensors to the Internet. Gateways act as both wireless access points and routers.
IoT wireless sensor technology has enabled applications across numerous industries, offering endless possibilities for IoT connectivity. Some of the many advantages of smart wireless sensors include:
- Real-time monitoring. Wireless sensors monitor their surroundings in real time, always providing up-to-date information.
- Risk minimization. Smart sensors pick up on irregular environmental stimuli such as leaks and temperature changes, minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Environmental maintenance. IoT sensors maintain favorable environments in the workplace, keeping track of elements such as the heat index and air quality.
- Long-lasting use. Wireless sensors can operate on a single battery for years without requiring charging or changing.
- Low maintenance. IoT sensors need very little maintenance, meaning you don’t have to worry about performing upkeep or scheduling repairs.
- Low power. Sensory hardware consumes low levels of power, which is why their batteries last for years at a time.
- Operative capabilities. Smart sensors can function on low-bandwidth networks due to their light data loads.
Our selection of wireless sensors works exceptionally well with LoRaWAN networks. LoRaWAN networks are popular for their ability to transmit data across long distances and excellent link margins that reach signals beneath the radio frequency (RF) noise floor. These networks make connections more accessible, proving useful for wireless sensors in remote areas without public access.
If you need IoT wireless sensors, MultiTech + Radio Bridge are your solution. As the leading LoRaWAN sensor manufacturer in North America, we’re always looking for ways to continue raising the bar in the IoT industry. Our sensors are built to last, embracing unbeatable functionality and efficiency across numerous applications. We also offer product customizations to better serve your organization’s needs. When you come to Radio Bridge for LoRaWAN wireless sensor solutions, we want you to have the best possible experience. That’s why we always strive to deliver excellent customer service that makes you feel comfortable and supported.
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are small devices that collect and share data gathered from their surroundings within a technological ecosystem. Sometimes the sensor can act on the data immediately or the data can be sent to an IoT gateway that aggregates and sends the data where it needs to go for further action and analysis.
Smart building IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental input and process that data in order to perform desired automated functions related to security, facilities management, or related property needs. Wireless MultiTech sensors that perform these functions include:
- Temperature sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Push button sensors
- Movement sensors
- Leak detection sensors
- Industrial sensors
An IoT Sensors are small devices that collect and share data gathered from their surroundings within a technological ecosystem. Sometimes the sensor can act on the data immediately or the data can be sent to an IoT gateway that aggregates and sends the data where it needs to go for further action and analysis.
 There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
There are a number of traditional wireless sensor protocols that enable connectivity between the sensors and these to gateway: –Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are some examples of this. In recent years, with the development of LPWANs, standards have started to shift to better accommodate the ever-growing number of connected devices being used in commercial settings.
LoRaWAN® is benefitted by its long range, deep penetration, and extended battery life. LoRaWAN standards are maintained by the LoRa Alliance, an open, non-profit association dedicated to promoting and supporting their global adoption.
The ability for these sensors to provide ultra long range communications to industry standard gateways is one of their biggest benefits. For example, MultiTech offers LoRaWAN IoT sensors as part of their Radio Bridge family of products including:, which includes:
- Wireless temperature sensors designed to accurately detect ambient air temperatures both indoors and out
- Wireless proximity sensors that provide high accuracy proximity detection with open architecture for flexible integration
- Wireless push button sensors that can be used as wearables, remote controls, or for emergency response and other button-push applications
- Wireless movement sensors that use ultra-sensitive internal accelerometers to detect movement or utilization of critical assets and react accordingly
- Wireless leak detection sensors that use probes to detect the presence of water and alert the network to divert potential catastrophe
- Wireless industrial sensors designed for industrial standards such as 4-20mA current loops, digital inputs, vibration and beyond
LoRaWAN IoT sensors low power consumption and long range transmit capabilities allow them to be used in a broad range of applications.
Here are some common use cases:
- Smart buildings. Modern offices, retail spaces, and factories can all benefit from smart building technology, including: temperature and humidity monitoring of critical rooms or assets, water leak detection to minimize leaking water or flood damage, motion detection to track utilization of high cost assets and more.
- Server room maintenance. Leak detection sensors can communicate automatically over wireless networks to notify IT managers when a leak is found in their liquid cooled server room, saving both precious data and precious dollars. Temperature sensing can ensure that critical IT equipment stays within its recommended operating ranges.
- Drug management. Readmission rates can be reduced and health outcomes improved via smart drug management and medication tracking using IoT sensors. Automated temperature monitoring of stored medications may improve medicine safety, effectiveness and compliance.
- Emergency response. Wireless push button sensors can be used in healthcare settings to allow nurses and caregivers to be alerted and respond to emergency patient needs in real time.
- Wind monitoring and control. Being able to monitor wind and solar energy generation in real time can prevent downtime and disruption, reducing risk and cost.
- Supply chain management. The right network solutions can help with shipment verification, remote monitoring of product storage, and the efficiency of logistical operations. That in turn leads to fewer shipping delays, less product loss, and happier customers.
- The benefits of using LoRaWAN IoT sensors are vast and unique to each industry they serve. All business applications of this technology lead to improved response time, improved compliance, decreased network downtime, performance data gathering, and ultimately–cost savings.
Check out MultiTech’s wireless LoRaWAN Sensor catalog for a closer look at this efficiency-boosting technology.
Smart Buildings
Smart building IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental input and process that data in order to perform desired automated functions related to security, facilities management, or related property needs. Wireless MultiTech sensors that perform these functions include:
- Temperature sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Push button sensors
- Movement sensors
- Leak detection sensors
- Industrial sensors
MultiTech smart building IoT sensor technology can help lead to fewer errors, faster response times, improved compliance, decreased downtime, and ultimately, cost savings. That’s because our equipment enables:
- Wireless failover
- Wireline replacement
- Parallel networking
- Remote equipment management and control
- Facility automation
- Secure data transfer
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are small devices that collect and share data gathered from their surroundings within a technological ecosystem. Sometimes the sensor can act on the data immediately or the data can be sent to an IoT gateway that aggregates and sends the data where it needs to go for further action and analysis.
Smart building IoT sensors are devices that collect environmental input and process that data in order to perform desired automated functions related to security, facilities management, or related property needs. Wireless MultiTech sensors that perform these functions include:
- Temperature sensors
- Proximity sensors
- Push button sensors
- Movement sensors
- Leak detection sensors
- Industrial sensors
A smart building is a facility that uses advanced technology and data analytics to optimize its operations, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the occupant experience. Smart buildings use a variety of sensors, devices, and systems to collect and analyze data on building operations, energy consumption, and occupant behavior. This data is then used to make informed decisions about building management, energy usage, and maintenance.
Smart buildings can include a wide range of systems and technologies, including:
- Building automation systems (BAS): These systems control the building’s mechanical and electrical systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and security.
- Energy management systems (EMS): These systems optimize energy usage and reduce energy waste by monitoring and controlling energy consumption.
- Occupancy sensors: These sensors detect the presence of occupants and adjust building systems accordingly, such as turning off lights in unoccupied rooms.
- Environmental sensors: These sensors monitor indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity to ensure optimal comfort and health for occupants.
- Building analytics software: This software collects and analyzes data from building systems and sensors to identify inefficiencies, optimize operations, and predict maintenance needs.
Smart buildings offer a number of benefits, including:
- Improved energy efficiency: Smart buildings can reduce energy waste by optimizing energy consumption and reducing energy usage during times of low occupancy.
- Enhanced occupant comfort and productivity: By adjusting building systems based on occupant behavior and preferences, smart buildings can create a more comfortable and productive environment for occupants.
- Predictive maintenance: Smart buildings can identify maintenance needs before they become critical, reducing downtime and improving equipment lifespan.
- Cost savings: By optimizing energy usage and reducing maintenance costs, smart buildings can result in significant cost savings over time.
Smart buildings represent a growing trend in building design and management, offering a wide range of benefits for both building owners and occupants.