IoT in Utilities
IoT connectivity is paving the way toward a better response to rapid urban development all around the world. MultiTech provides devices like gateways, routers and modems that help cities or buildings connect to the world around them. These devices give utilities the data they need to scale up thoughtfully and responsibly as their service areas continue to grow. Integrating IoT devices across distribution networks lets utilities connect the dots in real time so they can make better-informed decisions that lead to sustainable growth, smarter spending, and a better service for their customers.
Whether you’re running a local electrical utility or delivering water from the source, MultiTech’s IoT smart grid communication equipment helps keep you connected to your assets to facilitate:
- Water management systems
- Automated meter reading
- Dynamic demand response
- Environmental monitoring
- Emergency alerts

Key Benefits of Deploying a Managed Industrial Cellular Router for Private or Public Utilities
Remote and Hard-to-Reach Areas: Utilities often operate in remote locations, such as substations, pumping stations, or wind farms, where wired internet connections are unavailable or expensive to install. Industrial cellular routers offer reliable, wireless connectivity via 4G/5G networks in these areas.
Backup Connectivity: For utilities operating in urban environments, cellular routers can provide backup connectivity if wired connections (like fiber or DSL) fail, ensuring critical systems remain operational.
Remote Asset Monitoring: Utilities can use industrial cellular routers to monitor assets such as transformers, water pumps, or gas pipelines in real-time. This allows for early detection of problems, reducing the risk of outages or equipment failures.
SCADA Systems Integration: Cellular routers can enable seamless communication between remote assets and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems. This real-time data helps utilities to make informed operational decisions and respond quickly to emerging issues.
Control of Distributed Energy Resources (DER): Cellular routers can enable the real-time control of distributed energy resources, like solar panels, wind turbines, or energy storage systems, optimizing energy generation and distribution.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Deploying wired infrastructure (like fiber) to remote areas can be prohibitively expensive. Cellular routers can provide reliable connectivity without the need for extensive physical infrastructure, offering a cost-effective alternative.
Lower Operational Costs: Remote monitoring and management enabled by cellular routers reduce the need for onsite inspections and manual interventions, resulting in lower operational and maintenance costs.
Enhanced Network Security: Industrial cellular routers often come with built-in VPNs, firewalls, and encryption protocols, ensuring that communication between utilities’ critical infrastructure and central offices is secure. This is essential for protecting sensitive data and critical control systems from cyberattacks.
Private LTE Networks: Utilities can establish private LTE networks using industrial cellular routers, which offer better control, security, and reliability than public networks. These networks can be tailored specifically for utility needs, ensuring uptime and security.
Grid Modernization: Cellular routers can play a key role in enabling the transition to smart grids, which require real-time communication and control over distributed assets. These routers facilitate two-way communication between grid operators and energy consumers, enabling demand response, load balancing, and more efficient energy distribution.
Demand Response: With real-time communication enabled by cellular routers, utilities can implement demand response programs to adjust electricity usage during peak times, improving grid efficiency and reducing the need for additional power generation.
Data-Driven Decisions: Cellular routers allow utilities to collect and transmit real-time data from distributed assets, enabling more informed decision-making. Data analytics can help utilities optimize performance, predict equipment failures, and improve overall efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance: By continuously monitoring equipment performance data, utilities can use predictive maintenance to address issues before they result in costly failures or outages.
Applications and Real World Use Cases
Application: Many utilities use industrial cellular routers to monitor remote electrical substations, which are often located in rural or hard-to-reach areas.
Example: A U.S.-based utility provider, Southern California Edison, employs cellular routers to connect remote substations to their central monitoring systems. These routers provide real-time data on substation performance, helping them detect faults and maintain reliable power delivery without requiring physical presence.
Application: Utilities use industrial routers as part of their smart grid infrastructure to enable two-way communication between power generation, distribution systems, and smart meters.
Example: In the UK, Western Power Distribution utilizes cellular routers to create secure communication pathways for its smart grid initiatives. The routers help connect smart meters to the main control centers, allowing for real-time monitoring of electricity usage, load balancing, and integration with renewable energy sources.
Application: Cellular routers are used by water utilities to monitor and control pumping stations remotely. This helps ensure the reliable delivery of water and wastewater management.
Example: Sydney Water, Australia’s largest water utility, uses industrial cellular routers to provide connectivity for its remote pumping stations. These routers transmit data on water flow, pressure, and quality to centralized systems, allowing engineers to adjust operations in real-time and optimize water distribution.
Application: Utilities use industrial cellular routers to manage distributed energy resources like solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
Example: A renewable energy company in Germany uses cellular routers to manage its network of wind farms. These routers provide a reliable connection between remote wind turbines and the central control room, enabling real-time performance monitoring, data collection, and remote control of energy output to the grid.
Application: Gas utilities deploy cellular routers to support smart metering systems that allow for real-time monitoring of gas consumption and leak detection.
Example: In Italy, Eni Gas uses cellular routers in conjunction with smart meters to monitor gas consumption across urban and rural areas. The cellular connectivity ensures accurate and timely reporting to the utility, as well as automatic alerts in the case of a gas leak or anomaly.
Application: Cellular routers play a key role in integrating renewable energy sources into traditional energy grids, helping to balance supply and demand.
Example: Duke Energy in the United States uses cellular routers to integrate solar farms into its grid. These routers provide secure, real-time communication between the solar farm and the grid’s energy management systems, enabling efficient distribution of renewable energy based on current demand.
Application: During natural disasters or large-scale power outages, utilities deploy mobile units equipped with industrial cellular routers to maintain critical communication and power management.
Example: After hurricanes in the southeastern U.S., utilities such as Florida Power & Light deploy mobile generators and temporary substations with cellular routers to maintain communication with central operations. These routers provide critical data on power availability and help coordinate recovery efforts.
Application: Cellular routers are used to integrate remote SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems in water utilities, enabling centralized monitoring of water flow, reservoir levels, and water treatment plants.
Example: Veolia Water, a global leader in water management, uses industrial cellular routers in remote locations to provide connectivity to its SCADA systems. These routers allow for the real-time monitoring of water treatment plants, ensuring that water quality and pressure are maintained.
Application: Utilities use cellular routers to connect IoT sensors installed on critical assets such as transformers, valves, or generators. These sensors collect data on equipment performance, allowing utilities to perform predictive maintenance.
Example: A European energy company uses cellular routers to connect IoT-enabled sensors to its power transformers. The sensors track performance metrics such as temperature and vibration, with the data being sent to the central office through the cellular router. This system enables the utility to predict and prevent transformer failures.
Application: Industrial routers are used for automating load balancing across the grid, enabling utilities to adjust electricity distribution based on demand in real-time.
Example: Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E) in California uses cellular routers to automate its demand-response systems, adjusting energy distribution based on consumption peaks and integrating renewables efficiently. This minimizes energy waste and reduces the need for additional power generation.
Energy Companies Public and Private LTE Communications
IoT in Energy
Capacitor Bank Control, Reclosers and Pole Tilt Monitoring with MultiTech Public and Private LTE Connectivity Products
Whether monitoring a well, a pipeline or a refinery, governments around the world are in agreement that understanding exactly what’s happening in the production and distribution of fossil fuels is of paramount importance both for global continuity of energy production as well as for environmental protection. As critical infrastructure, it is exceedingly important to protect this process from digital interference from those with technical know-how and malicious intent.
Today’s so called “smart city” consists of a set of unrelated, purpose-built applications. Parking, traffic signaling, ambulance or police car location monitoring, public utilities, HVAC at schools and IoT for smart buildings … the list goes on and on. Savvy city managers need more than local interest groups to inform them about how to spend and how to save, and the Internet of Things promises to provide the cross-departmental knowledge they need to optimize taxpayer spend as well as public services.
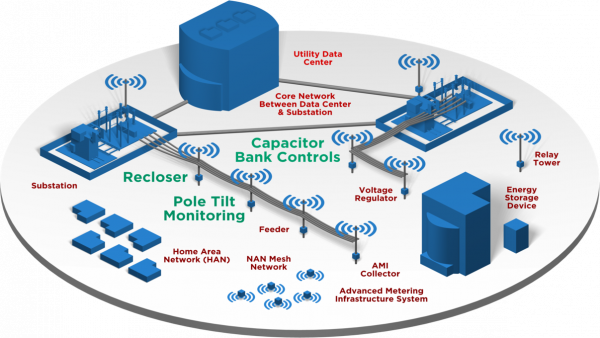
Wireless Communications Energy Program
Reliable, secure, cost-effective communications with your remote devices is critical to successful energy management and risk mitigation. Cellular IoT is rapidly expanding its coverage area and is becoming the standard for secure data communications.
In addition, the MultiTech portfolio will support emerging public/private LTE broadband cellular initiatives such as AT&T FirstNet, Anterix, CBRS,and 5G. When you need wireless communication for mission critical distribution automation, you can be certain that MultiTech devices will meet your needs now and well into the future.